Shopping Cart
0 item(s) - $0.00- Accortec, Inc.
- Addon Tech
- Advantech Co., Ltd
- Axiom
- BLACKBOX
- C2g
- Chief Manufacturing
- Cisco
- Dell
- EATON
- EMC
- Enet Components, Inc.
- Fortinet
- Getac, Inc
- HP
- HPE
- IBM
- Intel
- Legrand Group
- Lenovo
- Lexmark
- Middle Atlantic Products, Inc
- Monoprice, Inc
- National Products, Inc
- Panduit Corp
- StarTech.com
- Supermicro
- TDK
- Tripp Lite
- Veritas Technologies Llc
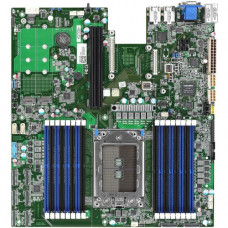
Tyan Tomcat SX S8026 Server Motherboard - AMD Chipset - Socket SP3 - 2 TB DDR4 SDRAM Maximum RAM - RDIMM, DIMM, LRDIMM, NVDIMM - 16 x Memory Slots - Gigabit Ethernet - 2 x USB 3.0 Port S8026GM2NRE
Add to Compare
Tyan s8026 Single Socket AMD EPYC Server MotherboardTyan''s Tomcat SX S8026 is an NVMe focused single socket AMD EPYC (Formerly codenamed "Naples") motherboard in an EATX form factor. Harnessing the power of a single AMD SP3 socket, the board is designed to deliver 2P performance within a 1P footprint. The motherboard is designed for traditional 2P workloads such as fast cloud storage, real time analytics, big data, e-commerce, and video streaming applications. It features support for high speed NVMe deployment with 64 PCIe lanes available near the front of the motherboard over eight PCIe x8 SFF-8611 Oculink connectors. By adopting an industry standard EATX form factor, the s8026 allows customers to deploy it with minimal integration efforts into existing chassis designs.Key FeaturesAMD EPYC 14nm CPUThe AMD EPYC processor offers the highest possible performance from a single CPU socket, including: Up to 32 CPU cores and 64 threads Support for up to 2TB total RAM per socket on all CPU models 128 PCIe lanes Dual Socket Feature SetTraditionally, the only way to deploy a large number of PCIe devices has been to select a dual-socket motherboard even if the compute demands of the server was low. Tyan has targeted these applications with the AMD EPYC platform by supporting up to 124 PCIe lanes and 8 memory channels in a single-socket platform. Significant savings can be had both in CPU cost and power consumption by migrating workloads to a single socket AMD EPYC platform.124 PCIe LanesThe s8026 motherboard was designed from the ground up to take full advantage of AMD''s Single-Socket I/O capabilities. The board exposes 124 PCIe lanes across a variety of connectors: (8) PCIe x8 SFF-8611 Oculink connectors for NVMe PCIe Gen 3.0 x24 Riser Card Slot PCIe Gen 3.0 x16 Riser Card Slot PCIe Gen 3.0 x16 OCP LAN Mezzanine PCIe Gen 3.0 x2 NVMe M.2 ports for OS drives 16 NVMe PortsNVMe technology offers breakthrough performance for SSDs by attaching storage devices directly to the PCIe bus, freeing them from the SATA protocol that was originally designed for slower rotational media. This technology significantly reduces storage latency and increases transfer speeds.To put things into perspective, during the summer of 2017 the fastest SATA SSDs on the market were already saturating the SATA 6G bus with peak sequential transfer rates of 550MB/s read and 520 MB/s write. The bigger pipe and lower latency of the NVMe PCIe x4 link allows the fastest NVMe SSDs to reach sequential read rates of 3,500MB/s and read rates around 2,100MB/s. Non-sequential performance heavily favors NVMe devices as well, with typical SATA SSDs achieving 4K random read/write performance around the 100K IOPS mark. In comparison, performance NVMe devices routinely offer 4K random R/W numbers in the neighborhood of 350-450K+ IOPS.Previous motherboard designs were not well suited to NVMe deployment due to a lack of PCIe lanes. Each NVMe device requires a PCIe x4 link. Large numbers of these devices could not previously be deployed without expensive and bottleneck inducing switch chips or without quickly running out of I/O resources for other devices in the server. The AMD EPYC CPU is ideal for this storage technology, featuring support for 128 PCIe lanes from a single CPU socket.
Technical Specifications:
Chipset Manufacturer: AMDTotal Processor Supported: 1Processor Socket: Socket SP3Processor Supported: EPYCNumber of Memory Slots: 16Memory Form Factor: RDIMM, DIMM, LRDIMM, NVDIMMMaximum Memory Supported: 2 TBMemory Technology: DDR4 SDRAMMemory Speed Supported: 2667 MHzController Type: Serial ATAOnboard Video: On-board Video ChipsetGraphics Controller Manufacturer: ASPEEDGraphics Controller Model: AST2500Gigabit Ethernet: YesNumber of Total Expansion Slots: 2Total Number of PCI Express Slots: 2Number of PCI Express x24 Slots: 2Total Number of USB Ports: 2Number of USB 3.0 Ports: 2VGA: YesNumber of M.2 Interfaces: 2Total Number of Onboard USB Ports: 3Number of Onboard USB 3.0 Ports: 1Number of NVMe Ports: 16Form Factor: Extended ATXWidth: 13"Depth: 12"Package Contents:
- Tomcat SX S8026 Single Socket AMD EPYC Server Motherboard, 1 x Quick Installation Guide, 1 x TYAN Device Driver CD
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: